Tech Support
9 Ways to Fix Blue Screen of Death PC and Laptop Errors
Key Takeaways
- The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) is a critical error on Windows PCs and laptops, often caused by hardware or software issues.
- Common fixes include restarting, updating drivers, checking hardware, and using Windows troubleshooting tools.
- Back up your data regularly to avoid data loss from BSOD crashes.
- Beginners can follow simple steps to diagnose and resolve BSOD errors.
Introduction to Blue Screen of Death PC and Laptop Issues

The Blue Screen of Death PC and laptop error, often called BSOD, is a dreaded sight for Windows users. It’s that moment when your screen turns blue, displays an error code, and your computer crashes. Don’t panic! This guide breaks down what causes the Blue Screen of Death, how to fix it, and how to prevent it. Whether you’re a beginner or a casual user, we’ll walk you through each step in plain English so you can get your PC or laptop back on track.
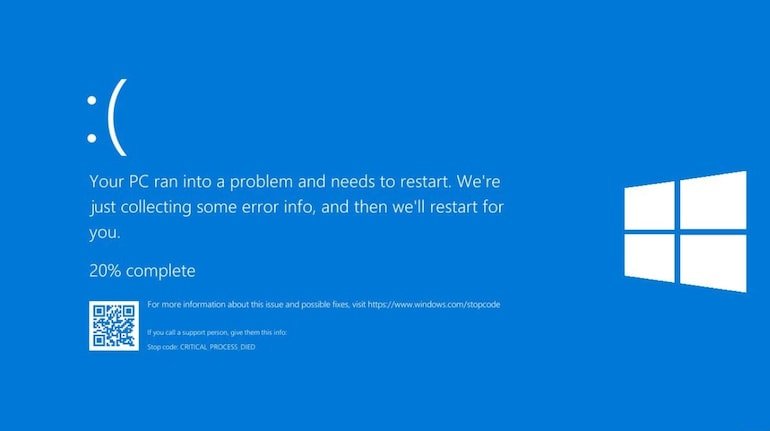
What Is the Blue Screen of Death?
The Blue Screen of Death is a Windows error screen that appears when your system encounters a critical issue it can’t recover from. It’s like your computer’s way of saying, “I’m in trouble!” The screen shows an error code, a sad face (in newer Windows versions), and sometimes a QR code. The BSOD stops your PC to prevent further damage, but it can be frustrating if you don’t know what’s causing it.
Common causes include:
- Faulty hardware (like RAM or hard drives)
- Outdated or corrupted drivers
- Software conflicts
- Malware infections
- Overheating
Why Does the Blue Screen of Death Happen?
Understanding why the BSOD occurs is the first step to fixing it. Here are the main culprits:
- Driver Issues: Drivers are like translators between your hardware and Windows. If they’re outdated or corrupted, they can trigger a BSOD.
- Hardware Problems: Faulty RAM, failing hard drives, or loose connections can cause crashes.
- Software Conflicts: Incompatible programs or recent updates can clash with your system.
- Malware: Viruses or malicious software can corrupt system files, leading to errors.
- Overheating: If your PC or laptop gets too hot, components may fail, causing a BSOD.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fix Blue Screen of Death PC and Laptop Issues
Let’s dive into how to troubleshoot and resolve the Blue Screen of Death. Follow these steps carefully, and you’ll likely get your system running smoothly again.
Step 1: Restart Your Computer
It sounds simple, but restarting can fix temporary glitches. Press and hold the power button to shut down your PC or laptop, then turn it back on. If the BSOD persists, move to the next step.
Step 2: Note the Error Code
When the BSOD appears, it usually displays an error code like “CRITICAL_PROCESS_DIED” or “IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL.” Write it down or take a photo. You can search for this code on Microsoft’s official support page to find specific fixes for your error.
Step 3: Boot into Safe Mode
Safe Mode starts Windows with minimal drivers and services, which can help you troubleshoot. To enter Safe Mode:
- Restart your PC and press F8 or Shift + F8 (or F11 on some systems) before the Windows logo appears.
- Select Safe Mode from the Advanced Boot Options menu.
- Once in Safe Mode, you can uninstall recent software, update drivers, or run scans.
Step 4: Update or Roll Back Drivers
Outdated or faulty drivers are a common BSOD cause. Here’s how to fix them:
- Open Device Manager (right-click the Start button and select it).
- Look for devices with a yellow triangle (indicating issues).
- Right-click the device, select Update driver, and choose Search automatically for drivers.
- If a recent driver update caused the issue, select Roll back driver instead.
You can also visit your laptop or PC manufacturer’s website (like Dell or HP) to download the latest drivers.
Step 5: Check for Windows Updates
Windows updates often include bug fixes for BSOD issues. To check:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Click Check for updates and install any available updates.
- Restart your computer after updating.
Step 6: Scan for Malware
Malware can corrupt system files and cause crashes. Use Windows Defender or a trusted antivirus like Malwarebytes to scan your system:
- Open Windows Defender (search for it in the Start menu).
- Run a full scan to check for viruses.
- Remove any threats found and restart your PC.
Step 7: Test Your Hardware
Faulty hardware like RAM or hard drives can trigger BSOD errors. Windows has built-in tools to help:
- Memory Diagnostic Tool: Search for “Windows Memory Diagnostic” in the Start menu and run it to test your RAM.
- Disk Check: Open Command Prompt (type cmd in the Start menu, select “Run as administrator”), and type
chkdsk /f C:. This checks your hard drive for errors.
If issues are found, consider replacing the faulty hardware or consulting a technician.
Step 8: Use System Restore
If the BSOD started after a recent change (like installing software), System Restore can revert your PC to a previous state:
- Search for “Create a restore point” in the Start menu.
- Click System Restore and follow the prompts to choose a restore point.
- Let Windows roll back to a time before the issue started.
Step 9: Reset or Reinstall Windows
If nothing else works, resetting or reinstalling Windows may be your last resort. This will erase your data, so back up your files first.
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
- Choose Reset this PC and follow the prompts.
- Alternatively, create a bootable USB from Microsoft’s Media Creation Tool for a fresh install.
How to Prevent Blue Screen of Death PC and Laptop Issues
Prevention is better than a cure! Here are tips to avoid BSOD errors:
- Keep Drivers Updated: Regularly check for driver updates via Device Manager or your manufacturer’s website.
- Run Regular Scans: Use antivirus software to catch malware early.
- Avoid Overheating: Clean your PC’s fans and vents to ensure proper airflow.
- Back Up Data: Use cloud services like Google Drive or external drives to protect your files.
- Install Trusted Software: Avoid downloading programs from sketchy websites to prevent conflicts.
FAQ About Blue Screen of Death PC and Laptop Issues
What does the Blue Screen of Death mean?
It’s a critical error in Windows that stops your PC to prevent damage, often caused by hardware or software issues.
Can a BSOD damage my computer?
No, the BSOD itself doesn’t harm your hardware, but it may indicate underlying issues that need fixing.
How do I find the BSOD error code?
The error code is displayed on the blue screen. Write it down or scan the QR code (if shown) for details.
Should I take my PC to a professional?
If you’ve tried the steps above and the BSOD persists, a technician can diagnose hardware issues or complex software problems.
Conclusion
The Blue Screen of Death PC and laptop errors can feel overwhelming, but with the right steps, you can troubleshoot and fix them. Start with simple solutions like restarting or updating drivers, then move to advanced options like Safe Mode or System Restore if needed. By keeping your system updated, scanning for malware, and maintaining your hardware, you can prevent future BSOD crashes. If you’re ever stuck, don’t hesitate to consult a professional or check Microsoft’s support resources. Stay calm, and you’ll have your PC running smoothly in no time!
Tech Support
WiFi Connected but No Internet: 6 Simple Fixes

Ever been hyped to binge-watch a new series or finish some work online, only to see that dreaded “WiFi connected but no internet” message? It’s like your device is teasing you—connected, yet totally useless! Don’t stress—this is a common hiccup for internet users, and I’m here to walk you through fixing it with easy, step-by-step solutions. Whether you’re on your phone, laptop, or tablet, these tips will help you get back online fast. Ready to say goodbye to that annoying error and hello to smooth browsing? Let’s jump right in! If you’re also struggling with phone storage, check out our guide on clearing system storage on Android.
Short Answer: To fix “WiFi connected but no internet,” restart your router, check signal strength, forget and reconnect to the network, update your device’s software, check for ISP outages, or reset network settings.
Key Takeaways:

- Restarting your router often resolves connectivity issues.
- Weak WiFi signals can cause “no internet” errors.
- Forgetting and reconnecting to WiFi refreshes the connection.
- Software updates can fix bugs affecting your internet.
- ISP outages might be the culprit—check with your provider.
- Resetting network settings is a last-ditch fix.
- Secure your WiFi and maintain your router to avoid future issues.
Restart Your Router

First things first—when your WiFi says it’s connected but there’s no internet, try restarting your router. It’s like giving your router a quick power nap to clear its head. Unplug it from the wall, wait about 30 seconds, and plug it back in. Most routers take a minute or two to reconnect. This simple trick fixes a ton of issues by resetting the connection and clearing glitches. For more router tips, check out Linksys’ guide on router troubleshooting. Still offline? Don’t worry, we’ve got more fixes coming up!
Check Your WiFi Signal Strength

A weak WiFi signal can leave you connected but without internet, like trying to hear a friend shouting from a mile away. Look at the WiFi bars on your device—fewer bars mean a weaker signal. Move closer to your router or clear away obstacles like walls or furniture. Electronics like microwaves or cordless phones can also mess with your signal, so keep your router in an open spot. If your signal’s still weak, learn more about boosting it at Netgear’s WiFi optimization guide. Ready for the next step? Let’s keep going.
Forget and Reconnect to the WiFi Network

Sometimes, your device holds onto a bad connection like a stubborn kid refusing to let go of a toy. To fix this, “forget” the WiFi network and reconnect. On your phone or laptop, go to WiFi Settings, find your network, and tap Forget Network. Then, select the network again and enter the password. You can usually find the password on your router’s sticker or in your ISP’s app. This refreshes the connection and often solves the “no internet” problem. Need help finding your password? Check out TP-Link’s guide on WiFi passwords. Still stuck? There’s more to try.
Update Your Device’s Software

Old software can cause connection issues, like trying to play a new game on an outdated console. Check for updates on your device to keep things running smoothly. On Android, go to Settings > System > System Update. For iPhones, head to Settings > General > Software Update. Laptops? Check Windows Update or macOS System Settings. Updating fixes bugs that might be blocking your internet. For detailed steps, visit Google’s Android update guide. If your software’s up-to-date and you’re still offline, let’s check something else.
Check for ISP Outages

Sometimes, the problem isn’t you—it’s your internet service provider (ISP). If they’re having an outage, your WiFi will connect but show no internet. Visit your ISP’s website or app for outage alerts. For example, Xfinity users can check xfinity.com/support/status. You can also call their support line or look for updates on social media. If there’s an outage, you’ll need to wait it out. No outage? Then it’s time for a bigger fix. Curious about what’s next? Let’s dive in.
Reset Network Settings
If nothing’s worked so far, resetting your network settings is like rebooting your device’s entire connection system. This clears WiFi, Bluetooth, and mobile data settings, so you’ll need to reconnect to networks afterward. On Android, go to Settings > System > Reset Options > Reset WiFi, Mobile & Bluetooth. On iPhones, it’s Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Reset > Reset Network Settings. Keep your WiFi password handy—you’ll need it! For more on resets, see Apple’s reset guide. Want to stop this from happening again? Read on.
Prevent Future WiFi Issues
Nobody wants to deal with “WiFi connected but no internet” again, right? Keep your router’s firmware updated—your ISP’s website or router manual will show you how. Use a strong WiFi password to block freeloaders who slow your network. Apps like Fing can show you who’s on your WiFi. Place your router in an open area, away from walls or electronics, for a better signal. Restart your router every few weeks to keep it fresh. For more tips on speeding up your internet, check out our guide on optimizing Android performance.
FAQs
Why does my WiFi say connected but no internet?
This happens due to router glitches, weak signals, outdated software, or ISP outages. Restart your router, check the signal, or update your device to fix it.
Will resetting network settings delete my photos or apps?
Nope! It only clears WiFi, Bluetooth, and mobile data settings. Your photos, apps, and other data are safe, but you’ll need to reconnect to WiFi.
How can I check if my ISP is down?
Visit your ISP’s website or app, like xfinity.com/support/status, or call their support line. Social media can also show outage updates.
Can a weak WiFi signal stop my internet?
Yes, a weak signal can connect but fail to load the internet. Move closer to your router or clear obstacles to boost the signal.
Conclusion
Getting hit with a “WiFi connected but no internet” error is a total bummer, but you’ve got this! Start with a quick router restart, check your signal, or forget and reconnect to the network. Keep your device updated, check for ISP outages, and reset network settings if you’re desperate. To avoid future headaches, update your router, secure your WiFi, and keep it in a good spot. With these steps, you’ll be back to streaming, gaming, or browsing in no time. For more tech fixes, explore our guide on clearing Android storage. Now, go conquer that WiFi!
Hardware Solutions
10 Fixes for Desktop Keep Restarting Problem
Key Takeaways:
- A desktop that keeps restarting is often caused by overheating, software issues, or hardware problems.
- Basic troubleshooting includes checking temperatures, updating drivers, and scanning for malware.
- Advanced steps involve inspecting hardware like RAM or the power supply.
- Regular maintenance can prevent future restarts.
Introduction

Desktop keep restarting issues can be incredibly frustrating, especially when you’re deep in work or gaming. That sudden reboot feels like your PC is throwing a fit, but don’t worry—there’s usually a straightforward fix. This guide breaks down why your desktop keeps restarting and walks you through 10 easy, beginner-friendly steps to solve it. Whether it’s a software glitch, overheating, or a hardware issue, we’ve got you covered with practical solutions. Let’s dive in and get your computer running smoothly again.
Why Does Your Desktop Keep Restarting?
Before fixing the problem, it helps to understand what’s causing it. A desktop that keeps restarting could be dealing with:
- Overheating: Components like the CPU or GPU get too hot, triggering a reboot to protect them.
- Software Issues: Outdated drivers, corrupted system files, or malware can cause crashes.
- Hardware Problems: Faulty RAM, a failing power supply, or loose connections might be to blame.
- Windows Settings: Automatic restarts after updates or errors can catch you off guard.
Identifying the root cause is the first step to stopping those annoying reboots.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix Desktop Keep Restarting
Here’s a clear, beginner-friendly guide to troubleshoot and fix your desktop keeping restarting issue. Follow these steps in order, and you’ll likely find the culprit.
Step 1: Check for Overheating
Overheating is a common reason desktops restart. When your CPU or GPU gets too hot, your PC reboots to prevent damage.
- What to do: Download a free tool like HWMonitor to check your CPU and GPU temperatures. Safe CPU temperatures are usually below 85°C (185°F) under load.
- Fix it: Clean your PC’s fans and vents with compressed air to remove dust. Ensure your computer is in a well-ventilated area. If temperatures are still high, consider reapplying thermal paste to the CPU or upgrading your cooling system.
Step 2: Update Your Drivers
Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause your desktop to restart unexpectedly. Drivers are like translators between your hardware and Windows, and when they’re outdated, things go haywire.
- What to do: Go to your computer manufacturer’s website (like Dell or HP) and download the latest drivers for your graphics card, motherboard, and other components.
- Pro tip: Use a tool like Driver Booster to automate driver updates if you’re not tech-savvy.
Step 3: Scan for Malware
Viruses or malware can mess with your system, causing random restarts.
- What to do: Run a full system scan using Windows Defender or a trusted antivirus like Malwarebytes. Make sure your antivirus is up to date before scanning.
- Fix it: Quarantine or remove any threats found. Restart your PC and check if the issue persists.
Step 4: Disable Automatic Restarts in Windows
Windows sometimes restarts automatically after errors or updates, which can feel like a random reboot.
- What to do:
- Right-click “This PC” (or “My Computer”) and select “Properties.”
- Click “Advanced system settings” > “Startup and Recovery” > “Settings.”
- Uncheck “Automatically restart” under System Failure.
- Why it helps: This stops Windows from rebooting during errors, letting you see error messages that might point to the cause.
Step 5: Check for Windows Updates
A buggy Windows update or missing patches can cause restarts.
- What to do: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and check for updates. Install any pending updates and restart manually.
- Note: If a recent update caused the issue, you can roll back to a previous version via Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
Step 6: Test Your RAM
Faulty RAM can cause your desktop to keep restarting.
- What to do: Use Windows’ built-in Memory Diagnostic Tool.
- Type “Windows Memory Diagnostic” in the search bar and open it.
- Choose “Restart now and check for problems.”
- Let the tool run—it’ll restart your PC and display results.
- Fix it: If errors are found, try reseating your RAM sticks or replacing faulty ones. Check your manufacturer’s website for compatible RAM.
Step 7: Inspect Your Power Supply Unit (PSU)
A failing PSU can cause random restarts by not delivering consistent power.
- What to do: Listen for unusual noises (like buzzing) from your PSU. If you’re comfortable, check that all PSU cables are securely connected.
- Fix it: If you suspect the PSU is faulty, take your PC to a technician or replace the PSU. Use a PSU calculator like OuterVision to ensure the new unit has enough wattage.
Step 8: **Protections**: This repairs corrupted Windows files that might be causing instability.
Step 8: Run System File Checker (SFC)
Corrupted system files can trigger restarts. Windows has a built-in tool to fix this.
- What to do:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator (search “cmd,” right-click, and select “Run as administrator”).
- Type
sfc /scannowand press Enter. - Wait for the scan to complete and follow any prompts to repair files.
- Why it helps: This repairs corrupted Windows files that might be causing instability.
Step 9: Check Event Viewer for Clues
Windows logs errors that can help pinpoint why your desktop keeps restarting.
- What to do:
- Type “Event Viewer” in the search bar and open it.
- Go to Windows Logs > System and look for “Error” or “Critical” events around the time of restarts.
- Note error codes and search them online for specific fixes.
- Example: A “Kernel-Power” error often points to PSU issues.
Step 10: Seek Professional Help
If none of the above work, your desktop keeping-restarting issue might need a pro. Hardware issues like a failing motherboard or GPU are tricky to diagnose without specialized tools.
- What to do: Contact your PC manufacturer’s support or a local technician. Provide them with any error codes from Event Viewer or Memory Diagnostic.
Preventing Future Restarts
To keep your desktop running smoothly:
- Clean regularly: Dust your PC every 3-6 months to prevent overheating.
- Update software: Keep Windows, drivers, and antivirus up-to-date.
- Monitor hardware: Use tools like HWMonitor to catch issues early.
- Backup data: Regularly back up files to avoid data loss during crashes.
FAQ
Q: Why does my desktop keep restarting randomly?
A: Random restarts are often caused by overheating, outdated drivers, malware, or hardware issues like faulty RAM or PSU. Follow the steps above to diagnose and fix.
Q: Can a virus cause my desktop to restart?
A: Yes, malware can destabilize your system, leading to restarts. Run a full antivirus scan to rule this out.
Q: How do I know if my PSU is failing?
A: Signs include random restarts, unusual noises from the PSU, or your PC shutting off under heavy load. A technician can confirm.
Q: Is it safe to clean my PC myself?
A: Yes, if you use compressed air and avoid touching sensitive components. If unsure, consult a professional.
Conclusion
A desktop keeping restarting problem can drive you up the wall, but with these 10 easy steps, you’re well-equipped to solve it. Start with simple fixes like checking for overheating or updating drivers, then move to advanced steps like testing RAM or the PSU. Regular maintenance can prevent future issues, keeping your PC stable and reliable. If you’re still stuck, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Got more questions? Drop them below, and let’s keep your desktop running like a champ!
Hardware Solutions
10 Simple Fixes for Your Frustrating Desktop Keep Restarting Issue

Meta Description: Discover 10 easy steps to fix your desktop’s keep-restarting issue. From overheating to software glitches, this beginner-friendly guide helps all PC users stop random reboots. (134 characters)
Key Takeaways:
- A desktop that keeps restarting is often caused by overheating, software issues, or hardware problems.
- Basic troubleshooting includes checking temperatures, updating drivers, and scanning for malware.
- Advanced steps involve inspecting hardware like RAM or the power supply.
- Regular maintenance can prevent future restarts.
Introduction

Desktop keep restarting issues can be incredibly frustrating, especially when you’re deep in work or gaming. That sudden reboot feels like your PC is throwing a fit, but don’t worry—there’s usually a straightforward fix. This guide breaks down why your desktop keeps restarting and walks you through 10 easy, beginner-friendly steps to solve it. Whether it’s a software glitch, overheating, or a hardware issue, we’ve got you covered with practical solutions. Let’s dive in and get your computer running smoothly again.
Why Does Your Desktop Keep Restarting?
Before fixing the problem, it helps to understand what’s causing it. A desktop that keeps restarting could be dealing with:
- Overheating: Components like the CPU or GPU get too hot, triggering a reboot to protect them.
- Software Issues: Outdated drivers, corrupted system files, or malware can cause crashes.
- Hardware Problems: Faulty RAM, a failing power supply, or loose connections might be to blame.
- Windows Settings: Automatic restarts after updates or errors can catch you off guard.
Identifying the root cause is the first step to stopping those annoying reboots.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix Desktop Keep Restarting
Here’s a clear, beginner-friendly guide to troubleshoot and fix your desktop keeping restarting issue. Follow these steps in order, and you’ll likely find the culprit.
Step 1: Check for Overheating
Overheating is a common reason desktops restart. When your CPU or GPU gets too hot, your PC reboots to prevent damage.
- What to do: Download a free tool like HWMonitor to check your CPU and GPU temperatures. Safe CPU temperatures are usually below 85°C (185°F) under load.
- Fix it: Clean your PC’s fans and vents with compressed air to remove dust. Ensure your computer is in a well-ventilated area. If temperatures are still high, consider reapplying thermal paste to the CPU or upgrading your cooling system.
Step 2: Update Your Drivers
Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause your desktop to restart unexpectedly. Drivers are like translators between your hardware and Windows, and when they’re outdated, things go haywire.
- What to do: Go to your computer manufacturer’s website (like Dell or HP) and download the latest drivers for your graphics card, motherboard, and other components.
- Pro tip: Use a tool like Driver Booster to automate driver updates if you’re not tech-savvy.
Step 3: Scan for Malware
Viruses or malware can mess with your system, causing random restarts.
- What to do: Run a full system scan using Windows Defender or a trusted antivirus like Malwarebytes. Make sure your antivirus is up to date before scanning.
- Fix it: Quarantine or remove any threats found. Restart your PC and check if the issue persists.
Step 4: Disable Automatic Restarts in Windows
Windows sometimes restarts automatically after errors or updates, which can feel like a random reboot.
- What to do:
- Right-click “This PC” (or “My Computer”) and select “Properties.”
- Click “Advanced system settings” > “Startup and Recovery” > “Settings.”
- Uncheck “Automatically restart” under System Failure.
- Why it helps: This stops Windows from rebooting during errors, letting you see error messages that might point to the cause.
Step 5: Check for Windows Updates
A buggy Windows update or missing patches can cause restarts.
- What to do: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and check for updates. Install any pending updates and restart manually.
- Note: If a recent update caused the issue, you can roll back to a previous version via Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
Step 6: Test Your RAM
Faulty RAM can cause your desktop to keep restarting.
- What to do: Use Windows’ built-in Memory Diagnostic Tool.
- Type “Windows Memory Diagnostic” in the search bar and open it.
- Choose “Restart now and check for problems.”
- Let the tool run—it’ll restart your PC and display results.
- Fix it: If errors are found, try reseating your RAM sticks or replacing faulty ones. Check your manufacturer’s website for compatible RAM.
Step 7: Inspect Your Power Supply Unit (PSU)
A failing PSU can cause random restarts by not delivering consistent power.
- What to do: Listen for unusual noises (like buzzing) from your PSU. If you’re comfortable, check that all PSU cables are securely connected.
- Fix it: If you suspect the PSU is faulty, take your PC to a technician or replace the PSU. Use a PSU calculator like OuterVision to ensure the new unit has enough wattage.
Step 8: **Protections**: This repairs corrupted Windows files that might be causing instability.
Step 8: Run System File Checker (SFC)
Corrupted system files can trigger restarts. Windows has a built-in tool to fix this.
- What to do:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator (search “cmd,” right-click, and select “Run as administrator”).
- Type
sfc /scannowand press Enter. - Wait for the scan to complete and follow any prompts to repair files.
- Why it helps: This repairs corrupted Windows files that might be causing instability.
Step 9: Check Event Viewer for Clues
Windows logs errors that can help pinpoint why your desktop keeps restarting.
- What to do:
- Type “Event Viewer” in the search bar and open it.
- Go to Windows Logs > System and look for “Error” or “Critical” events around the time of restarts.
- Note error codes and search them online for specific fixes.
- Example: A “Kernel-Power” error often points to PSU issues.
Step 10: Seek Professional Help
If none of the above work, your desktop keeping-restarting issue might need a pro. Hardware issues like a failing motherboard or GPU are tricky to diagnose without specialized tools.
- What to do: Contact your PC manufacturer’s support or a local technician. Provide them with any error codes from Event Viewer or Memory Diagnostic.
Preventing Future Restarts
To keep your desktop running smoothly:
- Clean regularly: Dust your PC every 3-6 months to prevent overheating.
- Update software: Keep Windows, drivers, and antivirus up-to-date.
- Monitor hardware: Use tools like HWMonitor to catch issues early.
- Backup data: Regularly back up files to avoid data loss during crashes.
FAQ
Q: Why does my desktop keep restarting randomly?
A: Random restarts are often caused by overheating, outdated drivers, malware, or hardware issues like faulty RAM or PSU. Follow the steps above to diagnose and fix.
Q: Can a virus cause my desktop to restart?
A: Yes, malware can destabilize your system, leading to restarts. Run a full antivirus scan to rule this out.
Q: How do I know if my PSU is failing?
A: Signs include random restarts, unusual noises from the PSU, or your PC shutting off under heavy load. A technician can confirm.
Q: Is it safe to clean my PC myself?
A: Yes, if you use compressed air and avoid touching sensitive components. If unsure, consult a professional.
Conclusion
A desktop keeping restarting problem can drive you up the wall, but with these 10 easy steps, you’re well-equipped to solve it. Start with simple fixes like checking for overheating or updating drivers, then move to advanced steps like testing RAM or the PSU. Regular maintenance can prevent future issues, keeping your PC stable and reliable. If you’re still stuck, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Got more questions? Drop them below, and let’s keep your desktop running like a champ!

 Hardware Solutions1 week ago
Hardware Solutions1 week agoPhone Overheating While Charging: Causes, Fixes, and Prevention

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Top 7 AI Tools (With Detailed Guide) That Every Small Business Should Try in 2025

 Android Tips & Tricks1 week ago
Android Tips & Tricks1 week agoThe Complete Step-by-Step Guide to Android Photo Recovery

 Hardware Solutions1 week ago
Hardware Solutions1 week agoLaptop Keyboard Not Working? Here’s How to Fix It

 Tech Support1 week ago
Tech Support1 week agoWhy Is My WiFi Disconnecting Frequently? Causes & Solutions

 Hardware Solutions7 days ago
Hardware Solutions7 days agoPC Powers On But No Display? Quick Fixes Explained

 Tech Support5 days ago
Tech Support5 days agoHow to Fix Stick Drift on PS5: A Simple Guide for PC Gamers

 Game4 days ago
Game4 days agoHow to Optimize Your PC for Gaming in 2025


































