Hardware Solutions
10 Fixes for Desktop Keep Restarting Problem
Key Takeaways:
- A desktop that keeps restarting is often caused by overheating, software issues, or hardware problems.
- Basic troubleshooting includes checking temperatures, updating drivers, and scanning for malware.
- Advanced steps involve inspecting hardware like RAM or the power supply.
- Regular maintenance can prevent future restarts.
Introduction

Desktop keep restarting issues can be incredibly frustrating, especially when you’re deep in work or gaming. That sudden reboot feels like your PC is throwing a fit, but don’t worry—there’s usually a straightforward fix. This guide breaks down why your desktop keeps restarting and walks you through 10 easy, beginner-friendly steps to solve it. Whether it’s a software glitch, overheating, or a hardware issue, we’ve got you covered with practical solutions. Let’s dive in and get your computer running smoothly again.
Why Does Your Desktop Keep Restarting?
Before fixing the problem, it helps to understand what’s causing it. A desktop that keeps restarting could be dealing with:
- Overheating: Components like the CPU or GPU get too hot, triggering a reboot to protect them.
- Software Issues: Outdated drivers, corrupted system files, or malware can cause crashes.
- Hardware Problems: Faulty RAM, a failing power supply, or loose connections might be to blame.
- Windows Settings: Automatic restarts after updates or errors can catch you off guard.
Identifying the root cause is the first step to stopping those annoying reboots.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix Desktop Keep Restarting
Here’s a clear, beginner-friendly guide to troubleshoot and fix your desktop keeping restarting issue. Follow these steps in order, and you’ll likely find the culprit.
Step 1: Check for Overheating
Overheating is a common reason desktops restart. When your CPU or GPU gets too hot, your PC reboots to prevent damage.
- What to do: Download a free tool like HWMonitor to check your CPU and GPU temperatures. Safe CPU temperatures are usually below 85°C (185°F) under load.
- Fix it: Clean your PC’s fans and vents with compressed air to remove dust. Ensure your computer is in a well-ventilated area. If temperatures are still high, consider reapplying thermal paste to the CPU or upgrading your cooling system.
Step 2: Update Your Drivers
Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause your desktop to restart unexpectedly. Drivers are like translators between your hardware and Windows, and when they’re outdated, things go haywire.
- What to do: Go to your computer manufacturer’s website (like Dell or HP) and download the latest drivers for your graphics card, motherboard, and other components.
- Pro tip: Use a tool like Driver Booster to automate driver updates if you’re not tech-savvy.
Step 3: Scan for Malware
Viruses or malware can mess with your system, causing random restarts.
- What to do: Run a full system scan using Windows Defender or a trusted antivirus like Malwarebytes. Make sure your antivirus is up to date before scanning.
- Fix it: Quarantine or remove any threats found. Restart your PC and check if the issue persists.
Step 4: Disable Automatic Restarts in Windows
Windows sometimes restarts automatically after errors or updates, which can feel like a random reboot.
- What to do:
- Right-click “This PC” (or “My Computer”) and select “Properties.”
- Click “Advanced system settings” > “Startup and Recovery” > “Settings.”
- Uncheck “Automatically restart” under System Failure.
- Why it helps: This stops Windows from rebooting during errors, letting you see error messages that might point to the cause.
Step 5: Check for Windows Updates
A buggy Windows update or missing patches can cause restarts.
- What to do: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and check for updates. Install any pending updates and restart manually.
- Note: If a recent update caused the issue, you can roll back to a previous version via Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
Step 6: Test Your RAM
Faulty RAM can cause your desktop to keep restarting.
- What to do: Use Windows’ built-in Memory Diagnostic Tool.
- Type “Windows Memory Diagnostic” in the search bar and open it.
- Choose “Restart now and check for problems.”
- Let the tool run—it’ll restart your PC and display results.
- Fix it: If errors are found, try reseating your RAM sticks or replacing faulty ones. Check your manufacturer’s website for compatible RAM.
Step 7: Inspect Your Power Supply Unit (PSU)
A failing PSU can cause random restarts by not delivering consistent power.
- What to do: Listen for unusual noises (like buzzing) from your PSU. If you’re comfortable, check that all PSU cables are securely connected.
- Fix it: If you suspect the PSU is faulty, take your PC to a technician or replace the PSU. Use a PSU calculator like OuterVision to ensure the new unit has enough wattage.
Step 8: **Protections**: This repairs corrupted Windows files that might be causing instability.
Step 8: Run System File Checker (SFC)
Corrupted system files can trigger restarts. Windows has a built-in tool to fix this.
- What to do:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator (search “cmd,” right-click, and select “Run as administrator”).
- Type
sfc /scannowand press Enter. - Wait for the scan to complete and follow any prompts to repair files.
- Why it helps: This repairs corrupted Windows files that might be causing instability.
Step 9: Check Event Viewer for Clues
Windows logs errors that can help pinpoint why your desktop keeps restarting.
- What to do:
- Type “Event Viewer” in the search bar and open it.
- Go to Windows Logs > System and look for “Error” or “Critical” events around the time of restarts.
- Note error codes and search them online for specific fixes.
- Example: A “Kernel-Power” error often points to PSU issues.
Step 10: Seek Professional Help
If none of the above work, your desktop keeping-restarting issue might need a pro. Hardware issues like a failing motherboard or GPU are tricky to diagnose without specialized tools.
- What to do: Contact your PC manufacturer’s support or a local technician. Provide them with any error codes from Event Viewer or Memory Diagnostic.
Preventing Future Restarts
To keep your desktop running smoothly:
- Clean regularly: Dust your PC every 3-6 months to prevent overheating.
- Update software: Keep Windows, drivers, and antivirus up-to-date.
- Monitor hardware: Use tools like HWMonitor to catch issues early.
- Backup data: Regularly back up files to avoid data loss during crashes.
FAQ
Q: Why does my desktop keep restarting randomly?
A: Random restarts are often caused by overheating, outdated drivers, malware, or hardware issues like faulty RAM or PSU. Follow the steps above to diagnose and fix.
Q: Can a virus cause my desktop to restart?
A: Yes, malware can destabilize your system, leading to restarts. Run a full antivirus scan to rule this out.
Q: How do I know if my PSU is failing?
A: Signs include random restarts, unusual noises from the PSU, or your PC shutting off under heavy load. A technician can confirm.
Q: Is it safe to clean my PC myself?
A: Yes, if you use compressed air and avoid touching sensitive components. If unsure, consult a professional.
Conclusion
A desktop keeping restarting problem can drive you up the wall, but with these 10 easy steps, you’re well-equipped to solve it. Start with simple fixes like checking for overheating or updating drivers, then move to advanced steps like testing RAM or the PSU. Regular maintenance can prevent future issues, keeping your PC stable and reliable. If you’re still stuck, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Got more questions? Drop them below, and let’s keep your desktop running like a champ!
Hardware Solutions
10 Simple Fixes for Your Frustrating Desktop Keep Restarting Issue

Meta Description: Discover 10 easy steps to fix your desktop’s keep-restarting issue. From overheating to software glitches, this beginner-friendly guide helps all PC users stop random reboots. (134 characters)
Key Takeaways:
- A desktop that keeps restarting is often caused by overheating, software issues, or hardware problems.
- Basic troubleshooting includes checking temperatures, updating drivers, and scanning for malware.
- Advanced steps involve inspecting hardware like RAM or the power supply.
- Regular maintenance can prevent future restarts.
Introduction

Desktop keep restarting issues can be incredibly frustrating, especially when you’re deep in work or gaming. That sudden reboot feels like your PC is throwing a fit, but don’t worry—there’s usually a straightforward fix. This guide breaks down why your desktop keeps restarting and walks you through 10 easy, beginner-friendly steps to solve it. Whether it’s a software glitch, overheating, or a hardware issue, we’ve got you covered with practical solutions. Let’s dive in and get your computer running smoothly again.
Why Does Your Desktop Keep Restarting?
Before fixing the problem, it helps to understand what’s causing it. A desktop that keeps restarting could be dealing with:
- Overheating: Components like the CPU or GPU get too hot, triggering a reboot to protect them.
- Software Issues: Outdated drivers, corrupted system files, or malware can cause crashes.
- Hardware Problems: Faulty RAM, a failing power supply, or loose connections might be to blame.
- Windows Settings: Automatic restarts after updates or errors can catch you off guard.
Identifying the root cause is the first step to stopping those annoying reboots.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix Desktop Keep Restarting
Here’s a clear, beginner-friendly guide to troubleshoot and fix your desktop keeping restarting issue. Follow these steps in order, and you’ll likely find the culprit.
Step 1: Check for Overheating
Overheating is a common reason desktops restart. When your CPU or GPU gets too hot, your PC reboots to prevent damage.
- What to do: Download a free tool like HWMonitor to check your CPU and GPU temperatures. Safe CPU temperatures are usually below 85°C (185°F) under load.
- Fix it: Clean your PC’s fans and vents with compressed air to remove dust. Ensure your computer is in a well-ventilated area. If temperatures are still high, consider reapplying thermal paste to the CPU or upgrading your cooling system.
Step 2: Update Your Drivers
Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause your desktop to restart unexpectedly. Drivers are like translators between your hardware and Windows, and when they’re outdated, things go haywire.
- What to do: Go to your computer manufacturer’s website (like Dell or HP) and download the latest drivers for your graphics card, motherboard, and other components.
- Pro tip: Use a tool like Driver Booster to automate driver updates if you’re not tech-savvy.
Step 3: Scan for Malware
Viruses or malware can mess with your system, causing random restarts.
- What to do: Run a full system scan using Windows Defender or a trusted antivirus like Malwarebytes. Make sure your antivirus is up to date before scanning.
- Fix it: Quarantine or remove any threats found. Restart your PC and check if the issue persists.
Step 4: Disable Automatic Restarts in Windows
Windows sometimes restarts automatically after errors or updates, which can feel like a random reboot.
- What to do:
- Right-click “This PC” (or “My Computer”) and select “Properties.”
- Click “Advanced system settings” > “Startup and Recovery” > “Settings.”
- Uncheck “Automatically restart” under System Failure.
- Why it helps: This stops Windows from rebooting during errors, letting you see error messages that might point to the cause.
Step 5: Check for Windows Updates
A buggy Windows update or missing patches can cause restarts.
- What to do: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and check for updates. Install any pending updates and restart manually.
- Note: If a recent update caused the issue, you can roll back to a previous version via Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
Step 6: Test Your RAM
Faulty RAM can cause your desktop to keep restarting.
- What to do: Use Windows’ built-in Memory Diagnostic Tool.
- Type “Windows Memory Diagnostic” in the search bar and open it.
- Choose “Restart now and check for problems.”
- Let the tool run—it’ll restart your PC and display results.
- Fix it: If errors are found, try reseating your RAM sticks or replacing faulty ones. Check your manufacturer’s website for compatible RAM.
Step 7: Inspect Your Power Supply Unit (PSU)
A failing PSU can cause random restarts by not delivering consistent power.
- What to do: Listen for unusual noises (like buzzing) from your PSU. If you’re comfortable, check that all PSU cables are securely connected.
- Fix it: If you suspect the PSU is faulty, take your PC to a technician or replace the PSU. Use a PSU calculator like OuterVision to ensure the new unit has enough wattage.
Step 8: **Protections**: This repairs corrupted Windows files that might be causing instability.
Step 8: Run System File Checker (SFC)
Corrupted system files can trigger restarts. Windows has a built-in tool to fix this.
- What to do:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator (search “cmd,” right-click, and select “Run as administrator”).
- Type
sfc /scannowand press Enter. - Wait for the scan to complete and follow any prompts to repair files.
- Why it helps: This repairs corrupted Windows files that might be causing instability.
Step 9: Check Event Viewer for Clues
Windows logs errors that can help pinpoint why your desktop keeps restarting.
- What to do:
- Type “Event Viewer” in the search bar and open it.
- Go to Windows Logs > System and look for “Error” or “Critical” events around the time of restarts.
- Note error codes and search them online for specific fixes.
- Example: A “Kernel-Power” error often points to PSU issues.
Step 10: Seek Professional Help
If none of the above work, your desktop keeping-restarting issue might need a pro. Hardware issues like a failing motherboard or GPU are tricky to diagnose without specialized tools.
- What to do: Contact your PC manufacturer’s support or a local technician. Provide them with any error codes from Event Viewer or Memory Diagnostic.
Preventing Future Restarts
To keep your desktop running smoothly:
- Clean regularly: Dust your PC every 3-6 months to prevent overheating.
- Update software: Keep Windows, drivers, and antivirus up-to-date.
- Monitor hardware: Use tools like HWMonitor to catch issues early.
- Backup data: Regularly back up files to avoid data loss during crashes.
FAQ
Q: Why does my desktop keep restarting randomly?
A: Random restarts are often caused by overheating, outdated drivers, malware, or hardware issues like faulty RAM or PSU. Follow the steps above to diagnose and fix.
Q: Can a virus cause my desktop to restart?
A: Yes, malware can destabilize your system, leading to restarts. Run a full antivirus scan to rule this out.
Q: How do I know if my PSU is failing?
A: Signs include random restarts, unusual noises from the PSU, or your PC shutting off under heavy load. A technician can confirm.
Q: Is it safe to clean my PC myself?
A: Yes, if you use compressed air and avoid touching sensitive components. If unsure, consult a professional.
Conclusion
A desktop keeping restarting problem can drive you up the wall, but with these 10 easy steps, you’re well-equipped to solve it. Start with simple fixes like checking for overheating or updating drivers, then move to advanced steps like testing RAM or the PSU. Regular maintenance can prevent future issues, keeping your PC stable and reliable. If you’re still stuck, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Got more questions? Drop them below, and let’s keep your desktop running like a champ!
Hardware Solutions
10 Easy Steps to Quiet Fan Noises on PC

Key Takeaways
- Fan noises in PCs are often caused by dust, loose parts, or failing components.
- Simple fixes include cleaning fans, securing loose screws, and adjusting fan speeds.
- Regular maintenance can prevent loud fan noises and keep your PC cool.
- Beginners can follow these steps to troubleshoot and reduce fan noise issues.
Introduction to Fan Noises

Fan noises can turn your PC experience into a noisy nightmare. That loud whirring, buzzing, or grinding from your computer can be distracting, whether you’re working, gaming, or just browsing. For all PC users, this guide is here to help! We’ll explain why fan noises happen, walk you through easy steps to fix them, and share tips to keep your PC quiet. Let’s silence that racket and get your computer running smoothly!
What Are Fan Noises?
Fan noises refer to any unusual or loud sounds coming from the cooling fans in your PC or laptop. These sounds might include whirring, rattling, buzzing, or grinding, and they’re a sign something’s off with your cooling system. Fans are crucial for keeping your PC’s components cool, but when they get noisy, it can mean trouble. For all PC users, loud fan noises can be annoying but are usually fixable with some basic troubleshooting.
Common causes of fan noises include:
- Dust buildup on fan blades
- Loose screws or components
- Worn-out fan bearings
- High fan speeds due to overheating
- Poor airflow or blocked vents
Why Do Fan Noises Happen?
To quiet those fan noises, it helps to know what’s causing them. Here’s the scoop:
- Dust Buildup: Dust on fan blades or vents can make fans work harder, creating noise.
- Loose Parts: Vibrating screws or loose fan mounts can cause rattling or buzzing.
- Worn Bearings: Over time, fan bearings wear out, leading to grinding or whining sounds.
- Overheating: If your PC runs hot, fans spin faster, increasing noise levels.
- Poor Airflow: Blocked vents or cluttered cases can force fans to overwork, making them louder.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fix Fan Noises on Your PC
Let’s dive into fixing those fan noises. These steps are beginner-friendly and designed for all PC users to quiet their systems without breaking a sweat.
Step 1: Power Off and Inspect Your PC
Before touching anything, safety first!
- Shut down your PC and unplug it from the power source.
- Open the case (for desktops) or check vents (for laptops) to look for obvious issues like loose cables or debris.
- Listen for the source of the noise when you restart later to pinpoint which fan is the culprit (CPU, GPU, or case fan).
Step 2: Clean the Fans and Vents
Dust is a common cause of fan noises. Here’s how to clean:
- Use a can of compressed air to blow dust off fan blades and vents. Hold fans still to avoid spinning them too fast.
- For stubborn dust, use a soft brush or cotton swab (never use water).
- For laptops, focus on cleaning the exhaust vents and fan grilles.
- Restart your PC and check if the noise is reduced.
Tip: Wear an anti-static wrist strap or touch a grounded metal surface to avoid static damage.
Step 3: Check for Loose Parts
Rattling or buzzing often comes from loose screws or components. To fix:
- Tighten screws on fans, the case, or other components using a screwdriver.
- Ensure the fan is securely mounted to its bracket or heatsink.
- Check for loose cables inside the case that might be hitting the fan blades.
- Restart your PC to see if the fan noises are gone.
Step 4: Monitor Fan Speeds
Fans running too fast can be noisy, especially if your PC is overheating. To check:
- Download a free tool like HWMonitor to view fan speeds and temperatures.
- If fans are spinning too fast (e.g., over 2000 RPM), your PC might be too hot.
- Adjust fan speeds using your PC’s BIOS or software like SpeedFan for desktops (check your motherboard manual for BIOS access).
- For laptops, avoid blocking vents by using a hard, flat surface instead of a bed or couch.
Step 5: Update Drivers and BIOS
Outdated drivers or BIOS can cause fans to misbehave. To update:
- Right-click the Start button and select Device Manager.
- Expand system devices and update any chipset or cooling-related drivers.
- Visit your PC manufacturer’s website (e.g., Dell or HP) to download the latest BIOS or firmware updates.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully, as BIOS updates can be risky if done incorrectly.
Step 6: Check for Overheating
Overheating makes fans work harder, increasing fan noises. To diagnose:
- Use HWMonitor to check CPU and GPU temperatures (ideal is below 80°C under load).
- If temperatures are high, ensure proper airflow by clearing vents and removing obstructions.
- For desktops, consider adding case fans or reapplying thermal paste to the CPU (consult a pro if unsure).
- For laptops, use a cooling pad to improve airflow.
Step 7: Scan for Malware
Malware can overwork your system, causing overheating and loud fans. To check:
- Open Windows Defender (search for it in the Start menu).
- Run a full scan under Virus & threat protection.
- Alternatively, use trusted antivirus software like Malwarebytes.
- Restart your PC after removing any threats, and check for noise reduction.
Step 8: Replace Faulty Fans
If a fan is still noisy (e.g., grinding or whining), it might be failing. To replace:
- Identify the noisy fan (CPU, GPU, or case fan) by listening or using software like HWMonitor.
- Purchase a compatible replacement fan (check your PC’s manual or manufacturer’s website for specs).
- For desktops, replace the fan yourself if comfortable, or hire a technician. For laptops, professional repair is recommended due to complexity.
- Check warranty options on your PC or components before replacing.
Step 9: Optimize Case Airflow
Poor airflow can make fans louder. For desktops:
- Ensure intake and exhaust fans are balanced (intake at the front, exhaust at the back/top).
- Remove unnecessary clutter like cables inside the case to improve airflow.
- Keep your PC in a well-ventilated area, away from walls or enclosed spaces.
For laptops, elevate the device slightly with a stand or cooling pad.
Step 10: Reset Windows (Last Resort)
If software issues are causing overheating and fan noises, resetting Windows might help. Back up your files first, as this may erase data.
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
- Select Reset this PC and choose whether to keep files or remove everything.
- Follow the prompts to reset. For a fresh install, use Microsoft’s Media Creation Tool.
How to Prevent Fan Noises
Keep your PC quiet with these tips for all PC users:
- Clean Regularly: Dust fans and vents every 3-6 months to prevent buildup.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use tools like HWMonitor to catch overheating early.
- Update Software: Keep drivers and BIOS updated via your manufacturer’s website.
- Improve Airflow: Ensure your PC has clear vents and is in a well-ventilated space.
- Back Up Data: Use cloud services like Google Drive to protect files in case of hardware issues.
FAQ About Fan Noises
Why are my PC fans so loud all of a sudden?
Sudden fan noises can be caused by dust buildup, overheating, or loose components.
Can fan noises damage my PC?
No, but loud fans may signal overheating, which can harm components if not addressed.
How do I know which fan is making noise?
Use software like HWMonitor or listen closely to pinpoint the noisy fan (CPU, GPU, or case).
Should I replace a noisy fan myself?
For desktops, you can replace fans if comfortable; for laptops, consult a professional due to complexity.
Conclusion
Fan noises can be a real buzzkill, but they’re often fixable with these beginner-friendly steps. From cleaning dust to adjusting fan speeds and checking for overheating, you can quiet your PC and keep it running cool. Regular maintenance—like dusting fans and monitoring temperatures—can prevent fan noises from coming back. If the noise persists or you suspect a failing fan, check your manufacturer’s support or consult a technician. Here’s to a quieter, cooler PC experience!
Hardware Solutions
Dysfunctional USB Port: How to Fix and Prevent Issues on Your PC
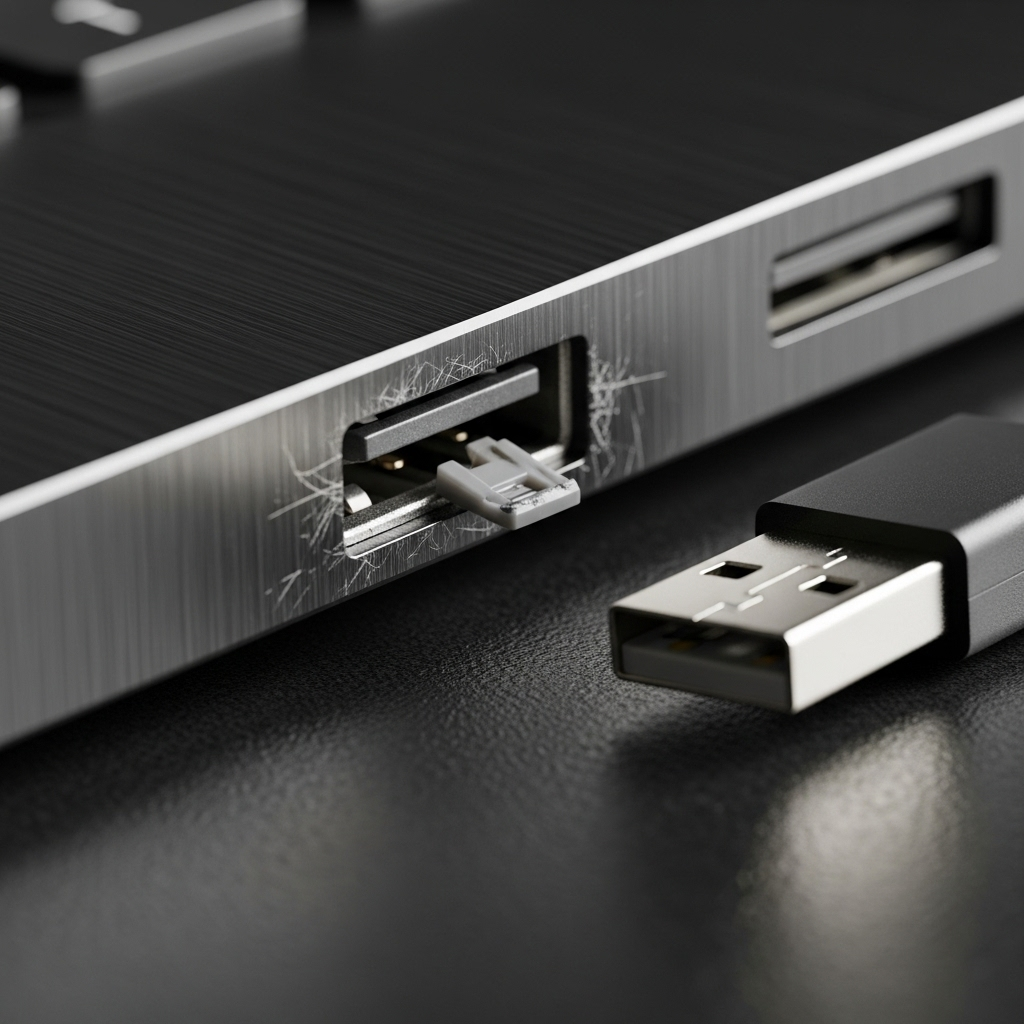

Key Takeaways
- A dysfunctional USB port can stop devices like flash drives or keyboards from working.
- Common fixes include checking connections, updating drivers, and inspecting for physical damage.
- Regular maintenance and careful handling can prevent USB port issues.
- Beginners can follow these steps to troubleshoot and resolve USB port problems.
Introduction to Dysfunctional USB Port
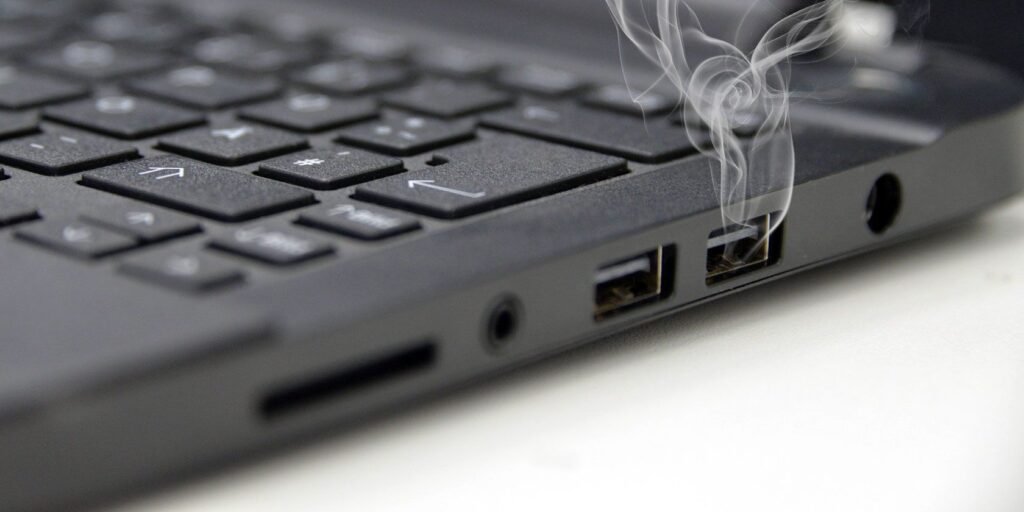

Dysfunctional USB port issues can be a real pain for PC users. You plug in your flash drive, keyboard, or phone, and nothing happens—or worse, it connects and disconnects randomly. Don’t fret! This guide is designed for all PC users, whether you’re a beginner or just dealing with tech casually. We’ll walk you through why USB ports go haywire, how to fix them step-by-step, and how to keep them working smoothly. Let’s get those ports back in action!
What Is a Dysfunctional USB Port?
A dysfunctional USB port is a USB port on your PC or laptop that doesn’t work properly. It might fail to recognize devices, provide power, or maintain a stable connection. For all PC users—whether you’re transferring files, charging gadgets, or connecting peripherals—this can disrupt your workflow. The good news? Most dysfunctional USB port issues are fixable with some basic troubleshooting.
Common causes of dysfunctional USB port issues include:
- Loose or damaged connections
- Outdated or corrupted USB drivers
- Physical damage to the port
- Power management settings issues
- Software conflicts or malware
Why Do Dysfunctional USB Ports Happen?
To fix a dysfunctional USB port, it’s helpful to know what’s causing the problem. Here’s the breakdown:
- Physical Damage: Bent pins, debris, or wear from heavy use can break a port.
- Driver Issues: Outdated or corrupted USB drivers can prevent ports from working.
- Power Problems: Some ports may not supply enough power for high-demand devices.
- Software Conflicts: Recent updates or programs can interfere with USB functionality.
- Malware: Viruses can mess with system settings, causing USB issues.
- Overloaded Ports: Too many devices plugged in can strain your PC’s USB system.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fix a Dysfunctional USB Port
Let’s roll up our sleeves and tackle that dysfunctional USB port. These steps are beginner-friendly and tailored for all PC users to get your ports working again.
Step 1: Check the Physical Connection
A loose or damaged connection is often the culprit. Here’s what to do:
- Unplug the USB device and inspect the port for debris, bent pins, or damage.
- Gently clean the port with a dry, soft brush or compressed air to remove dust.
- Plug the device into a different USB port on your PC to see if it works.
- Test the device on another PC to rule out a faulty device.
Note: Avoid forcing a plug into a damaged port, as this can worsen the issue.
Step 2: Restart Your PC
A simple restart can fix temporary glitches. Click Start > Power > Restart, then plug in your USB device again to check if the dysfunctional USB port is working. If not, move to the next step.
Step 3: Update USB Drivers
Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause dysfunctional USB port issues. To update:
- Right-click the Start button and select Device Manager.
- Expand Universal Serial Bus controllers.
- Right-click each USB-related entry (e.g., USB Root Hub) and select Update driver.
- Choose Search automatically for drivers.
- If no updates are found, visit your PC manufacturer’s website (e.g., Dell or HP) to download the latest USB or chipset drivers.
- Restart your PC after updating.
Step 4: Check Power Management Settings
Some USB ports turn off to save power, causing issues. To adjust:
- In Device Manager, right-click a USB Root Hub and select Properties.
- Go to the Power Management tab.
- Uncheck Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power.
- Repeat for all USB Root Hubs, then test the port again.
Step 5: Test with a Different USB Device
Sometimes the device, not the port, is the problem. Plug in a different USB device (like a mouse or flash drive) into the dysfunctional USB port. If it works, the original device might be faulty. If no devices work, the port itself is likely the issue.
Step 6: Scan for Malware
Malware can disrupt USB functionality. To check:
- Open Windows Defender (search for it in the Start menu).
- Run a full scan under Virus & threat protection.
- Alternatively, use trusted antivirus software like Malwarebytes to detect and remove threats.
- Restart your PC after removing any malware.
Step 7: Uninstall and Reinstall USB Controllers
If drivers are corrupted, reinstalling them can help. Here’s how:
- In Device Manager, expand Universal Serial Bus controllers.
- Right-click each USB controller and select Uninstall device.
- Restart your PC—Windows will automatically reinstall the drivers.
- Test the dysfunctional USB port after the restart.
Step 8: Check for Windows Updates
Windows updates can fix bugs causing dysfunctional USB port issues. To update:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Click Check for updates and install any available updates.
- Restart your PC and test the port.
Step 9: Inspect for Hardware Damage
If the port still doesn’t work, it might be physically damaged. For laptops or desktops:
- Examine the port closely with a flashlight for bent pins or debris.
- If comfortable, use a non-conductive tool (like a plastic spudger) to gently adjust bent pins.
- If the port is damaged beyond repair, consider using another port or a USB hub. For severe cases, consult a technician.
Step 10: Reset Windows (Last Resort)
If all else fails, resetting Windows can resolve deep software issues. Back up your files first, as this may erase data.
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
- Select Reset this PC and choose whether to keep files or remove everything.
- Follow the prompts to reset. For a fresh install, use Microsoft’s Media Creation Tool.
How to Prevent Dysfunctional USB Port Issues
Keep your USB ports in tip-top shape with these tips for all PC users:
- Handle with Care: Plug and unplug devices gently to avoid damaging pins.
- Keep Ports Clean: Regularly clean ports with compressed air to prevent debris buildup.
- Update Drivers: Check for driver updates monthly via Device Manager or your PC manufacturer’s website.
- Limit Overload: Avoid plugging too many devices into one port—use a powered USB hub if needed.
- Back Up Data: Use cloud services like Google Drive to protect files in case of major issues.
FAQ About Dysfunctional USB Port Issues
Why is my USB port not recognizing devices?
A dysfunctional USB port might have loose connections, outdated drivers, or physical damage.
Can a dysfunctional USB port damage my devices?
A damaged port might not supply proper power or data, but it’s unlikely to harm devices. Test devices on another port to be safe.
How do I know if my USB port is broken?
If no devices work in the port but function in others, or if you see physical damage, the port may be broken.
When should I seek professional help for a dysfunctional USB port?
If troubleshooting doesn’t work or the port is physically damaged, a technician can diagnose and repair hardware issues.
Conclusion
A dysfunctional USB port can throw a wrench in your PC experience, but most issues are fixable with these beginner-friendly steps. From checking connections to updating drivers and inspecting for damage, you can get your ports working again. Regular maintenance—like keeping ports clean and drivers updated—can prevent future problems. If you’re still stuck, check your manufacturer’s support resources or consult a pro. Here’s to hassle-free USB connections for all your devices!

 Hardware Solutions1 week ago
Hardware Solutions1 week agoPhone Overheating While Charging: Causes, Fixes, and Prevention

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Top 7 AI Tools (With Detailed Guide) That Every Small Business Should Try in 2025

 Android Tips & Tricks1 week ago
Android Tips & Tricks1 week agoThe Complete Step-by-Step Guide to Android Photo Recovery

 Hardware Solutions6 days ago
Hardware Solutions6 days agoPC Powers On But No Display? Quick Fixes Explained

 Hardware Solutions1 week ago
Hardware Solutions1 week agoLaptop Keyboard Not Working? Here’s How to Fix It

 Tech Support1 week ago
Tech Support1 week agoWhy Is My WiFi Disconnecting Frequently? Causes & Solutions

 Tech Support4 days ago
Tech Support4 days agoHow to Fix Stick Drift on PS5: A Simple Guide for PC Gamers

 Game4 days ago
Game4 days agoHow to Optimize Your PC for Gaming in 2025
























